HEARING CARE
Blocked Ear Tube: What It Feels Like, Why It Happens, and How It’s Managed
By Team Hearzap | Feb. 3, 2026
That “stuck” ear feeling after a cold, a bike ride in winter air, or a flight can be frustrating. Many people try to swallow, yawn, or chew to make the ear pop. Sometimes it helps, sometimes it doesn’t. In everyday language, this is often an ear tube blocked problem, usually involving the Eustachian tube. Most cases improve with time and simple measures, but knowing the warning signs matters.
What Is a Blocked Ear Tube?
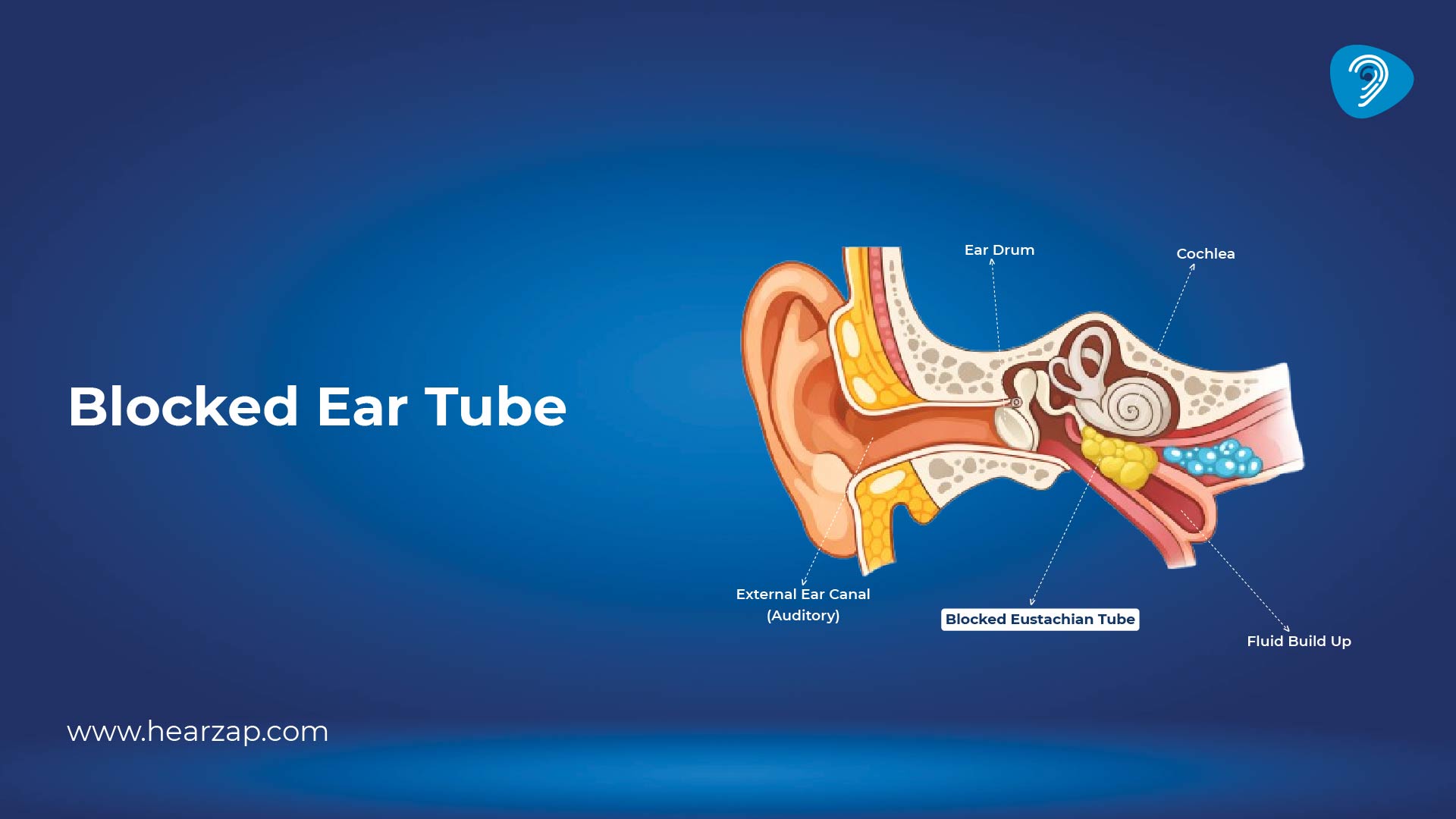
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and upper throat. It equalises pressure across the eardrum and drains fluid from the middle ear. When it doesn’t open well, pressure builds, fluid may collect, and sound can feel muffled. A quick look at ear anatomy explains why: the tube is narrow, lined with delicate tissue, and easily swollen by infection or allergies.
Ear Eustachian Tube Blocked – Meaning Explained
An ear eustachian tube blocked episode means the tube is swollen, narrowed, or briefly stuck closed. With poor ventilation, the middle ear develops negative pressure, the eardrum can pull slightly inward, and you feel tightness or fullness. If blockage persists, fluid can form behind the eardrum, adding crackling or a “water in the ear” sensation.
What Does a Blocked Ear Tube Feel Like?
Some people notice it only during swallowing; others feel it all day. It often follows viral colds, sinus congestion, dust exposure, or seasonal allergies – common triggers across India. The most typical sensations are pressure, heaviness, and reduced clarity. If you already have hearing loss, even mild muffling can feel pronounced and irritating.
Blocked Ear Eustachian Tube Symptoms
The phrase “blocked ear eustachian tube symptoms” includes:
- Fullness or pressure in one or both ears
- Muffled hearing or a “cotton” sensation
- Clicking, popping, or crackling with swallowing
- Mild ache or discomfort (often more pressure than pain)
- Light-headedness or slight imbalance
- Symptoms that worsen with flights, hills, or lifts
- Hearing your own voice louder than usual
If symptoms start with a cold and ease within a few days, it’s usually temporary.
How to Know if Ear Tube Is Blocked
People often search “how to know if ear tube is blocked” because it can mimic other issues. Safe clues include patterns: the feeling worsens with a blocked nose and improves as congestion settles; swallowing briefly changes the pressure; altitude shifts make it worse. Avoid putting cotton buds, oils, or random drops into the ear. If symptoms persist, an ear exam and a hearing test can separate Eustachian tube problems from ear-canal wax, infection, or other conditions.
Types of Ear Tube Blockage
Different phrases describe the same pathway, but they hint at where you feel pressure or what triggered it. Clinically, most relate to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Nose to Ear Tube Blocked
A nose-to-ear tube blocked feeling is common with colds, sinus irritation, or allergic rhinitis. Swelling near the tube’s nasal opening limits airflow into the middle ear. Many notice it more on waking, when congestion pools.
Ear to Nose Tube Blocked
An ear-to-nose tube blocked sensation can appear after forceful nose blowing or sudden weather changes. The tube may open briefly and close again, causing on–off pressure and popping.
Tube From Ear to Throat Blocked
A tube from ear to throat blocked query often reflects throat-end irritation from a sore throat, post-nasal drip, or reflux. When nose and throat swelling happen together, the ear can feel dull and tight.
Inner Ear Tube Blocked
The term inner ear tube blocked is common, but there is no Eustachian-type tube inside the inner ear. People use it to describe deep pressure, ringing, or balance symptoms, which may need a different evaluation.
Blocked Inner Ear Tube
Likewise, a blocked inner ear tube usually means fullness that isn’t improving. If it lasts beyond two weeks, is one-sided repeatedly, or comes with spinning vertigo, get checked rather than self-treating.
Common Causes of a Blocked Ear Tube
Most blockages are caused by swelling around the tube opening, not a hard plug inside the tube. Triggers also explain why the problem often returns.
Ear Wax Blocked Eustachian Tube
The term ‘ear wax blocked eustachian tube’ reflects a common misconception. Wax forms in the ear canal (in front of the eardrum), while the Eustachian tube sits behind the eardrum. However, wax can still cause muffling that feels similar to pressure. If wax is suspected, avoid home tools that can push it deeper or scratch the canal.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (Blocked Ear)
Eustachian tube dysfunction is the medical term for poor pressure equalisation. It’s commonly triggered by viral colds, sinusitis, allergies, smoke exposure, and sudden altitude changes. In adults over 50, age-related hearing change like presbycusis may coexist, so a “blocked” feeling shouldn’t be assumed to be only congestion.
Can a Blocked Ear Tube Lead to Other Problems?
Short-lived blockage is usually uncomfortable rather than dangerous. Longer blockage can allow fluid to collect, and that can lead to infection or ongoing muffling.
Can Blocked Eustachian Tube Cause Ear Infection?
Yes. When the tube stays closed, fluid can build behind the eardrum and become infected. Red flags include worsening pain, fever, thick discharge, or a child tugging at the ear.
Can Blocked Eustachian Tube Cause Ringing Ear?
It can. Pressure changes or middle-ear fluid may cause temporary tinnitus (ringing or buzzing). If ringing is sudden, one-sided, or paired with a marked hearing drop, it needs assessment.
How Is a Blocked Ear Tube Diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually begins with your history: cold or allergy symptoms, recent flying, recurrent episodes, or exposure to smoke/dust. A doctor examines the ear canal and eardrum and may assess middle-ear pressure (for example, with tympanometry). Some people start with an online hearing test as a screening step, but persistent symptoms should be confirmed with formal testing.
How Is a Blocked Ear Tube Managed?
Management depends on cause, severity, and duration. The aim is to reduce swelling, help the tube open naturally, and watch for complications.
Home Management for Mild Ear Tube Blockage
For mild symptoms linked to a cold or allergies, try:
- Frequent swallowing, warm fluids, or sugar-free gum
- Gentle yawning and jaw movements
- Steam inhalation or a warm shower
- Saline nasal rinses using sterile or boiled-and-cooled water
- Rest, hydration, and avoiding smoke exposure
Avoid forceful pressure manoeuvres if you have sharp pain, significant dizziness, or past eardrum problems.
Medical Treatment for Tube Blocked in Ear
For a tube blocked in ear that lasts or keeps returning, doctors focus on the driver. Allergies may need anti-allergy medicines and correctly used nasal steroid sprays over days to weeks. Suspected bacterial sinusitis or ear infection may need antibiotics based on examination.
Persistent fluid, frequent infections, or structural issues may require ENT review. If hearing is affected for longer, addressing hearing health matters too; some people may already use a hearing aid, and a fresh assessment helps optimise settings once the ear feels clear again.
Your doctor may also look for allergies, reflux, or nasal polyps that keep inflammation going. In some adults, a short course of medicines to reduce nasal swelling may be recommended, but it isn’t suitable for everyone (for example, people with uncontrolled blood pressure, glaucoma, pregnancy, or certain heart conditions).
If you’re using a nasal spray, technique matters: aim slightly outward within the nostril, not straight up the septum, and use it consistently. Avoid repeated forceful “popping” or aggressive nose blowing, which can irritate tissues.
If fluid persists or infections recur, procedures such as a tiny ventilation tube in the eardrum or balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube may be considered by an ENT specialist. If you have diabetes, immune issues, or use blood thinners, mention it early, because it can influence choices and monitoring during ongoing ear symptoms.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Seek medical advice if you have severe pain, fever, discharge, sudden hearing reduction, ongoing dizziness, facial weakness, or symptoms lasting more than 10-14 days. Also, get evaluated if it keeps recurring, affects only one ear repeatedly, or follows a head/ear injury.
Key Takeaways on Blocked Ear Tubes
Most “blocked ear” episodes happen when the Eustachian tube swells after colds, allergies, or pressure changes. Gentle home measures often help, and many people improve within a week. If symptoms persist, recur, or come with red flags, timely evaluation can prevent infection, reduce lingering fluid, and protect hearing.
FAQs
Is a Blocked Ear Tube Serious?
Usually not, especially if it follows a cold and improves steadily. It becomes more concerning if there is severe pain, fever, discharge, sudden hearing drop, or symptoms lasting beyond two weeks.
How Long Does a Blocked Ear Tube Last?
Many people recover in a few days to a week. If allergies are the trigger, symptoms may linger until inflammation is controlled. If you still feel blocked after 10–14 days, get assessed.
Can flying make it worse?
Yes. Rapid altitude changes can intensify pressure imbalance. If you must fly with congestion, ask a doctor about safe ways to reduce nasal swelling.
Should I try ear drops or oils?
Avoid self-medicating unless advised, particularly if there is pain or discharge. Some drops are unsafe if the eardrum is not intact.
Do children get this problem too?
Yes. Children have shorter, more horizontal Eustachian tubes, so colds can block them more easily. Persistent pain, fever, or reduced hearing should be checked.
Contact us
We are here for all your hearing needs, from hearing tests to hearing aids. Fill out the form below, and we will give you a call soon.
Please enter a valid mobile number with 10 digits.
Recent Blogs
By None | Feb. 2, 2026
By None | Jan. 30, 2026
By Team Hearzap | Jan. 28, 2026
By None | Jan. 27, 2026
By Team Hearzap | Jan. 23, 2026









