Generic
Ear Barotrauma
By Team Hearzap | Feb. 9, 2026
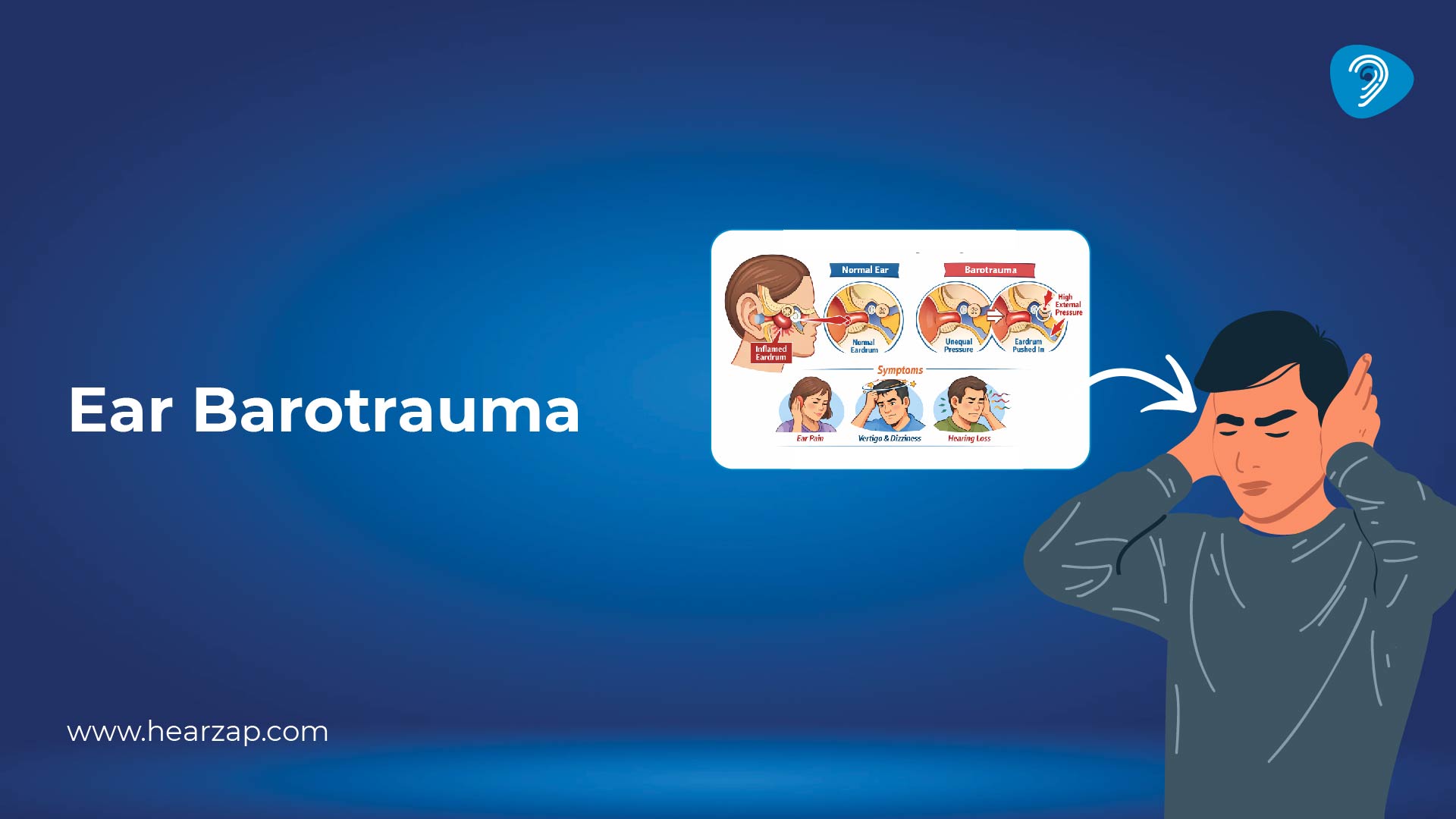
Ear Barotrauma: When Pressure Changes Make Your Ears Hurt
Almost everyone has felt it at some point. You’re on a flight, the plane starts descending, and suddenly your ears feel blocked. Swallowing doesn’t help. There’s pressure. Sometimes pain. Occasionally, it lingers even after you land.
That uncomfortable experience is often ear barotrauma. It happens when your ears can’t keep up with sudden pressure changes, and while it’s common, it can be unsettling when it doesn’t settle quickly.
The good news is that most cases heal well once you understand what’s happening and give your ears time to recover.
What Is Ear Barotrauma, Really?
Ear barotrauma occurs when external air pressure and middle ear pressure inside your body become unbalanced.
Your middle ear is an air-filled space. The Eustachian tube functions as a small passage which opens and closes to maintain comfort in this space. When that tube doesn’t open properly, pressure builds up.That’s when you feel pain, fullness, or muffled hearing.
This is why ear barotrauma is so common during flights, scuba diving, mountain drives, or any situation where pressure changes quickly.
What Does Ear Barotrauma Feel Like?
People describe ear barotrauma in different ways. For some, it’s just mild pressure. For others, it’s sharp and painful.
Common symptoms include:
- A blocked or full feeling in the ear
- Ear pain, especially during descent
- Muffled or reduced hearing
- Ringing in the ear
- Mild dizziness
In most cases, these symptoms ease once pressure equalises. But sometimes they linger, which is when people start to worry.
Inner Ear Barotrauma: Symptoms to Seriously Concern Over
More often, damage occurs only to the middle ear. However, in a few instances, the inner ear could also become barotraumatized, particularly during diving or extreme pressure changes.
This kind of damage can cause:
- Sudden Hearing Loss
- Severe Vertigo/Spinning Sensation
- Nausea/Vomiting
- Gait instability
In no way should inner ear barotrauma be overlooked. If giddiness is intense and keeps taunting a person, medical intervention must be sought.
Why Does Ear Barotrauma Happen to Some People More Than Others?
Certain situations make pressure equalisation harder:
- Flying or diving with a cold or sinus infection
- Nasal allergies or congestion
- Blocked Eustachian tubes
- Rapid pressure changes
Children experience ear barotrauma more easily because their Eustachian tubes are narrower and don’t open as efficiently.
How Doctors Identify Ear Barotrauma
Diagnosis usually starts with listening to your story — recent travel, diving, or altitude changes — followed by an ear examination.
An ENT doctor may:
- Look at the eardrum for redness or pressure changes
- Check for fluid behind the eardrum
- Assess hearing if symptoms persist
- Most cases don’t require scans or complex tests.
- Ear Barotrauma Treatment: What Actually Helps
Ear barotrauma treatment is mainly about helping the ear equalise pressure and reducing inflammation.
This may include:
- Nasal decongestants to open blocked passages
- Nasal steroid sprays for ongoing congestion
- Pain relief medication
- Gentle pressure-equalising techniques
The ear usually heals on its own once pressure normalises.
Is There an Ear Barotrauma Cure?
There’s no instant ear barotrauma cure, but that’s not a bad thing — because most cases resolve naturally.
Mild cases often improve within hours. Moderate cases may take a few days to a couple of weeks. Rest and patience play a big role in recovery.
Avoiding further pressure changes during healing is crucial.
Ear Barotrauma ICD 10
The medical code for ear barotrauma in ICD 10 (International Classification of Disease- 10) system exists under pressure-related injury codes which medical professionals use for their documentation needs. This method enables doctors to record and treat the medical condition with precise accuracy.
What to Avoid While Your Ear Heals
The recovery process requires you to stay away from these activities which are:
- The first activity is flying
- The second activity requires you to dive underwater
- The recovery process requires you to maintain dry ears
- The recovery process requires immediate treatment for nasal congestion
The process of healing will be delayed when you attempt to handle pressure changes before your body has finished healing.
How to Prevent Ear Barotrauma
The process of prevention through basic methods leads to successful results which require no extra work to achieve.
During flights passengers should perform three activities which include swallowing and yawning and chewing.
Passengers who experience nasal congestion should use nasal sprays before their travel.
Diving requires divers to perform pressure equalisation at a gradual pace.
The recovery process needs you to avoid travel while you are experiencing severe nasal congestion.
The combination of small daily behaviours produces an effect which becomes more significant.
When You Should See a Doctor
Seek medical care if:
- Pain is severe or worsening
- Hearing loss doesn’t improve
- Vertigo or imbalance develops
- Fluid or blood comes from the ear
These may signal complications or inner ear barotrauma.
Final Thoughts
Ear barotrauma is uncomfortable, sometimes painful, but usually temporary. It’s your ear’s way of telling you it needs time to adjust.
With the right ear barotrauma treatment, patience, and avoidance of further pressure changes, most people recover fully. There may not be a quick ear barotrauma cure, but the body heals remarkably well when given the chance.
Listening to your ears — especially during flights, dives, or pressure changes — goes a long way in protecting your hearing and comfort.
FAQs
How do you fix barotrauma in the ear?
Most ear barotrauma improves by relieving pressure with rest, nasal decongestants, gentle equalising, and giving the ear time to heal.
How long does ear barotrauma last?
Mild cases usually settle within hours or a few days, while more noticeable symptoms can take one to two weeks to fully resolve.
What is ear barotrauma?
Ear barotrauma is ear discomfort or injury caused by sudden pressure changes that the ear cannot adjust to quickly enough.
Is barotrauma reversible?
Yes, in most cases barotrauma is completely reversible, and hearing returns to normal once the ear heals properly.
Contact us
We are here for all your hearing needs, from hearing tests to hearing aids. Fill out the form below, and we will give you a call soon.
Please enter a valid mobile number with 10 digits.
Recent Blogs
By None | Feb. 7, 2026
By None | Feb. 6, 2026
By None | Feb. 5, 2026
By None | Feb. 4, 2026
By None | Feb. 3, 2026