Generic
Ear Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
By Team Hearzap | Dec. 30, 2025
If the skin in or around your ears keeps itching, flaking, or stinging, it can be surprisingly distracting. Many people in India blame sweat, headphones, or pollution, but recurring irritation is often ear eczema. This guide explains what it means, common eczema causes and eczema symptoms, and how sensible eczema treatment – at home and with medical help – can keep your ears more comfortable.
What Is Ear Eczema?
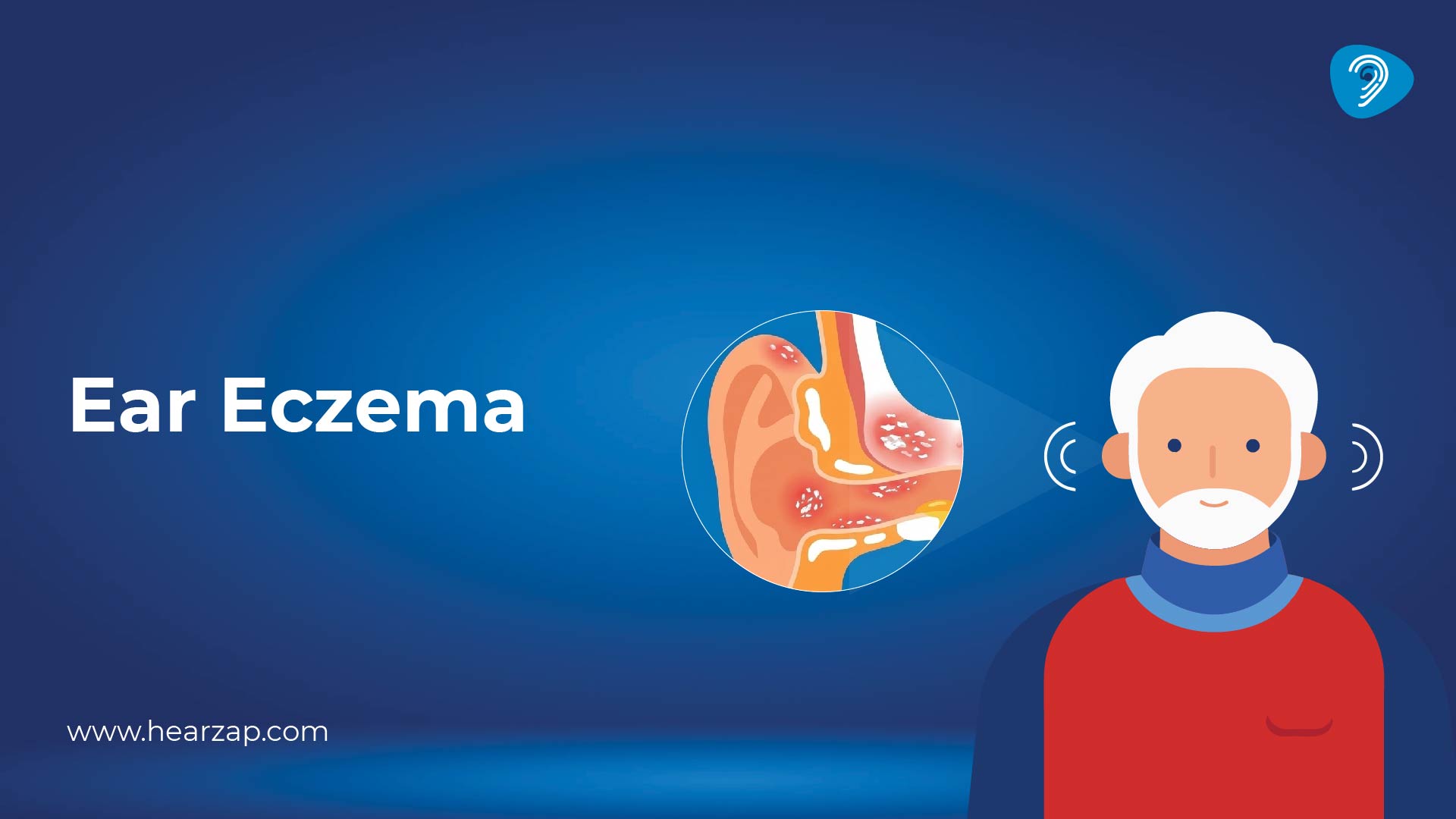
Ear eczema is an inflammatory skin condition that affects the outer ear, the ear canal, or the crease behind the ear. The skin becomes dry, red, or darker than usual and tends to itch a lot. In some people, the rash is mild and just looks like flaky skin at the edge of the ear. Others notice cracking, soreness, or even clear fluid.
Under a microscope, the skin barrier in ear eczema is thin and leaky. Moisture escapes quickly, and irritants slip in more easily. Certain patterns show up again and again: allergies, very dry skin, and a family history of sensitive skin or asthma. A specific dry type called asteatotic eczema is especially common in cold, dry months or in people who take very hot showers.
Common Causes of Ear Eczema
Ear eczema usually has more than one trigger, which is why flares often return if you only apply cream. Important eczema causes around the ear include:
- Nickel allergy from earrings or other jewellery.
- Irritation from hair dyes, shampoos, gels, or face wash running over the ear.
- Friction from helmets, dupattas, scarves, or tight masks rubbing the ear.
- Contact reaction to rubber or plastic earphone tips or the mould of a digital hearing device.
- Very dry skin, including asteatotic eczema, especially in North Indian winters or with strong air-conditioning.
- Weather swings, pollution, and sweat that make existing eczema symptoms more noticeable.
- Stress, poor sleep, or illness that lowers the skin’s tolerance.
Because the ear canal is narrow, trapped shampoo, hair oil, or water can also cause itching and ear canal infections. Many people remember one vigorous attempt at “cleaning” with buds or keys just before their ear eczema suddenly became worse.
Signs and Symptoms of Ear Eczema
The classic signs of eczema around the ear are easy to spot once you pause and examine the skin closely. Common features include:
- Persistent itching in or around the ear.
- Dry, rough, or flaky skin.
- Redness or dark patches during flare-ups.
- Cracks, soreness, or small crusts.
- A blocked or heavy feeling, sometimes with reduced hearing.
Cotton buds, hairpins, and pen caps make things worse by pushing wax in and scratching the surface, so the itch–scratch cycle continues, and stronger eczema treatment is often needed.
What is the difference between psoriasis and ear eczema?
Psoriasis and ear eczema can look similar, particularly when they sit close to the scalp, but they behave differently.
In psoriasis, ear patches are thicker, sharply edged, and covered with shiny scales, with similar lesions on the scalp, elbows, or knees and sometimes joint pain. In ear eczema, the skin is drier and itchier with softer borders, flaring after triggers such as new hair colour, harsh shampoo, or stress and settling with moisturisers and short courses of prescribed creams. A skin specialist will examine the rest of the body and the nails to decide whether you have psoriasis, ear eczema, or a combination of both.
Effective Ear Eczema Treatment Options
Once you know what triggers your flares, ear eczema treatment becomes simpler. Most people respond to a mix of targeted medicines and steady ear eczema treatment at home to keep the skin calm between flare-ups.
Medical Treatment Options
Depending on how severe your ear eczema is and whether there is an infection, a doctor may suggest:
- Short courses of mild steroid creams or ear drops to cut redness and swelling.
- Moisturisers or ceramide-based creams to rebuild the damaged skin barrier.
- Antifungal drops if there is dandruff or yeast in the canal.
- Antibiotic drops or tablets when there is pus, strong pain, or spreading infection.
- Antihistamine tablets at night to reduce itch and improve sleep.
Any drops used in the ear canal should be prescribed only after the eardrum has been checked. Sometimes debris or wax needs careful removal so medicines reach the skin properly and eczema symptoms settle faster.
Ear Eczema Treatment at Home
Thoughtful ear eczema treatment at home makes each flare shorter and milder. Safe options include:
- Using a warm compress on the outer ear for a few minutes to soothe itching.
- Gently cleansing around the ear with lukewarm water and a fragrance-free wash.
- Applying a thin layer of bland moisturiser, coconut oil, or aloe vera on the outer ear if advised.
- Avoiding obvious triggers such as nickel earrings, strong hair products, and rough straps.
- Running a humidifier in very dry rooms, especially in winter, to stop the skin from cracking.
Do not insert anything deep inside the ear canal – not buds, keys, or matchsticks. If itching, muffled hearing, or a blocked feeling continues, a hearing test can check whether wax, swelling, or fluid is interfering with sound before further eczema treatment is planned.
How to Prevent Ear Eczema
Good routines reduce how often ear eczema shows up. You can:
- Keep baths shorter and use lukewarm water so natural oils are not stripped away.
- Moisturise the skin around the ears every day, particularly after washing your hair.
- Avoid sharing earbuds, and wipe your own pair after gym sessions or crowded commutes.
- Treat scalp dandruff early so flakes and irritation do not spread to the ears.
- Manage stress with yoga, mindful breathing, or evening walks, since the skin often mirrors your emotional state.
- Wear breathable fabrics and avoid tight straps that constantly rub the ears.
If moisture sensitivity is high, tilt your head gently after a shower or swim so leftover water drains out. People who already use a hearing aid should ask how to keep both the device and the supporting skin clean without harsh chemicals.
When to See a Doctor?
While mild flares can be handled with moisturisers and simple eczema treatment, certain warning signs mean you should not delay:
- Severe pain in or around the ear.
- Discharge that is bloody, yellow, or foul-smelling.
- Sudden drop in hearing, ringing sounds, or dizziness.
- Fever, headache, or swelling that spreads to the side of the face.
- Skin that does not improve after five to seven days of careful ear eczema treatment at home.
These features suggest complications such as middle-ear disease or spreading infection. Early help protects both your skin and your hearing. If you are unsure where to start, many people choose to book hearing test appointment and get their ears examined at the same visit.
Conclusion
Living with ear eczema can be tiring, especially when itching keeps you awake or makes headphones and jewellery uncomfortable. The aim is not perfection, but calm, manageable skin and reliable hearing. When you understand your triggers, follow everyday care routines, and stick with your eczema treatment plan, flare-ups usually become milder and less frequent. Do not ignore persistent discomfort; repeated scratching can damage the canal and, over time, increase the risk of communication problems from untreated ear infections.
If your ears have been troubling you for weeks, consider booking a review rather than trying to manage alone. A short discussion with a specialist, combined with sensible changes at home, is often enough to bring ear eczema treatment back on track.
FAQs
How can I get rid of eczema in my ears?
Ear eczema rarely disappears overnight, but it can be controlled. Avoid triggers, moisturise gently, and use prescribed creams or drops as directed. See your doctor if pain, discharge, or hearing loss appears.
Is ear eczema a fungus?
No. Ear eczema is an inflammatory skin problem, not a fungus. Damaged skin may get fungal or bacterial infection, so antifungal or antibiotic drops are sometimes added to eczema treatment.
What is the difference between psoriasis and eczema in the ears?
In psoriasis, ear patches are thicker, sharply edged, and covered with shiny scales, with similar lesions on the scalp or elbows. In ear eczema, the skin is drier, itchier, and more clearly linked to triggers such as products or weather.
How is ear eczema caused?
There is no single cause. Ear eczema is more common in people with allergies or sensitive skin, and flares are triggered by nickel jewellery, harsh hair products, over-cleaning, asteatotic eczema, and sudden shifts in temperature or humidity.
How to treat eczema in babies?
For babies, keep baths short, use mild fragrance-free cleansers, and moisturise around the ears. Never put oil or drops directly into the ear without advice, and agree on eczema treatment with a paediatrician.
Contact us
We are here for all your hearing needs, from hearing tests to hearing aids. Fill out the form below, and we will give you a call soon.
Please enter a valid mobile number with 10 digits.
Recent Blogs
By None | Feb. 16, 2026
By None | Feb. 9, 2026
By None | Feb. 7, 2026
By None | Feb. 6, 2026
By None | Feb. 5, 2026