Generic
Bullous Myringitis: A Painful Ear Infection That Affects the Eardrum
By Team Hearzap | Jan. 30, 2026
Some ear infections develop gradually. The other type of infection starts with immediate intense pain which people find difficult to overlook. Bullous myringitis stands as one particular medical condition which results in severe ear drum infection symptoms that produce extreme pain for brief periods.
People often mistake it for a routine ear infection at first. But bullous myringitis has a few distinct features that make it different, especially the level of pain it can cause.
The good news is that with timely diagnosis and proper care, most cases settle well without long-term problems.
What Is Bullous Myringitis?
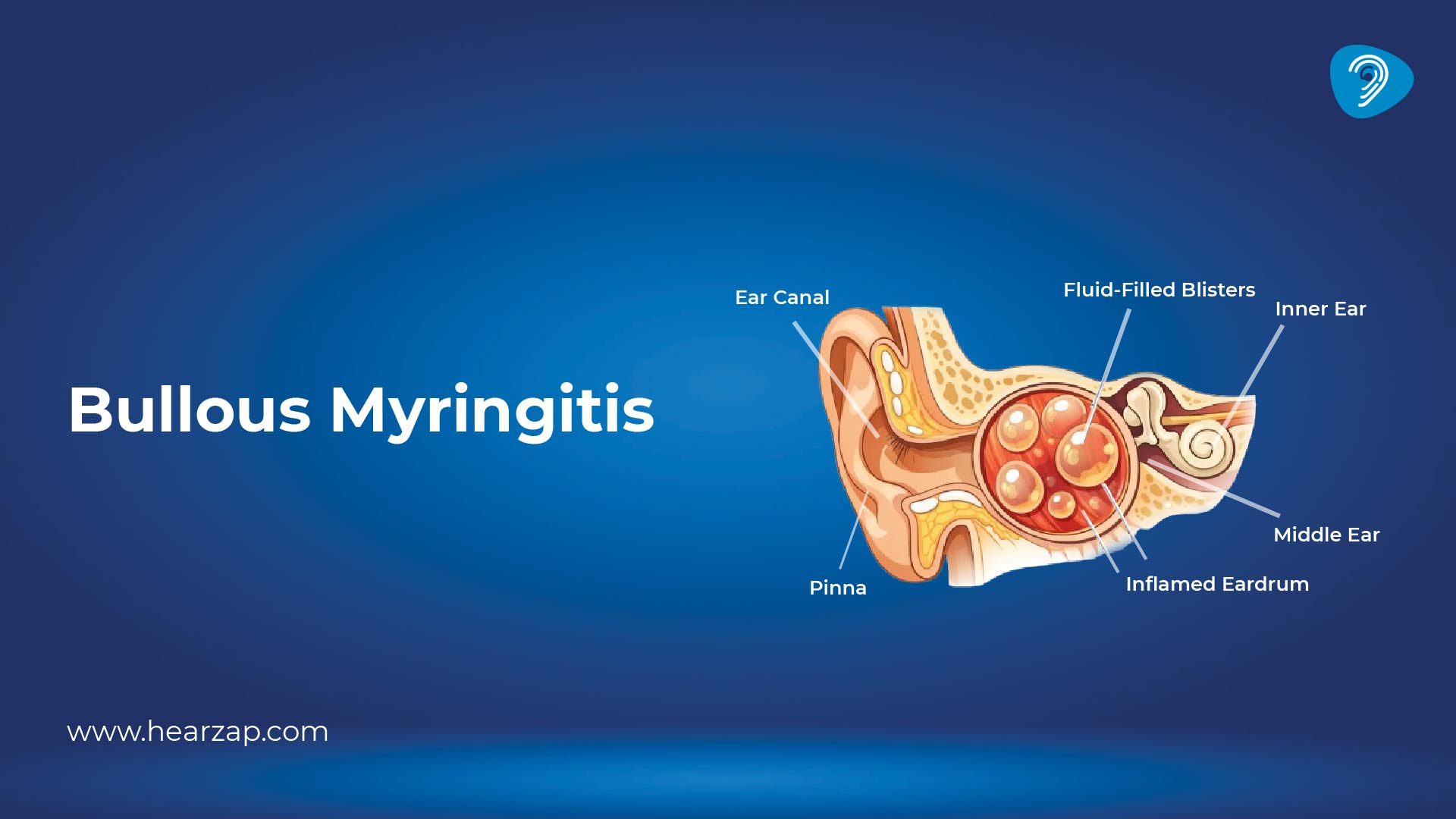
Bullous myringitis is an infection of the eardrum where fluid-filled blisters, called bullae, form on the surface of the tympanic membrane. These blisters can stretch the thin eardrum tissue, which is why the pain is often sharper than in a typical middle ear infection.
The infection may be caused by bacteria or viruses and sometimes appears alongside a middle ear infection rather than occurring alone.
Unlike standard ear infections that mainly involve fluid behind the eardrum, bullous myringitis directly irritates the eardrum surface itself.
What Does It Feel Like?
Patients with bullous myringitis usually describe pain that starts suddenly and feels deep and throbbing.
Common symptoms include:
- Sudden severe ear pain
- Reduced hearing on the affected side
- A feeling of pressure in the ear
- Ringing or sound sensitivity
- Occasionally mild fever
- Sometimes a small amount of blood-tinged discharge if a blister bursts
The pain can feel out of proportion compared to how the ear looks from the outside, which is one reason examination is important.
Why Does Bullous Myringitis Happen?
The condition develops when infection irritates the eardrum lining. The body responds with inflammation, and blisters form as fluid collects under the surface layer.
It may follow:
- A recent cold or upper respiratory infection
- Sinus congestion
- A middle ear infection
- Viral illnesses
Both children and adults can develop it, though the symptom pattern may differ slightly by age.
How It Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis is usually straightforward during an ear examination. An ENT doctor uses an otoscope to look at the eardrum and can often see the characteristic blisters.
Hearing tests are not always needed immediately but may be done if symptoms persist after treatment.
Because pain can be intense, early examination helps confirm the cause and start relief quickly.
Bullous Myringitis Treatment
Bullous myringitis treatment focuses on three main goals: controlling infection, relieving pain, and protecting hearing.
Treatment options include:
- Pain relief medication is often the mainstay of management
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Ear drops might be applied in some cases
- Oral medications in case of infection
The management issues are supposed to control pain, anticipating that the pain may be more marked during the first days.
Bullous Myringitis Antibiotics: When Are They Needed?
Not every case requires bullous myringitis antibiotics, but they are commonly prescribed when bacterial infection is likely or when symptoms are severe.
Doctors consider:
- Fever
- Severity of pain
- Signs of middle ear infection
- Patient age and risk factors
If the cause is viral, antibiotics may not help, but they are often used when it’s difficult to distinguish early on.
Bullous Myringitis Treatment in Adults
Bullous myringitis treatment in adults usually focuses strongly on pain control along with infection management.
Adults often report sharper pain but fewer systemic symptoms than children. Treatment plans typically include:
- Stronger pain relievers if needed
- Oral medication when infection is suspected
- Follow-up examination to confirm healing
Most adults improve noticeably within a few days once treatment begins.
Recovery Timeline
The pain typically peaks early and starts settling in 1 or 2 days after treatment the voice may be somewhat muffled for a short period while limp inflammations are clearing.
Full recovery usually takes 1 to 2 weeks.
While recovering:
- Keep the ear dry.
- Avoid putting anything in the ear.
- Take the prescribed medications according to the prescription.
It is important to follow up with the loose ends if the symptoms continue.
Bullous Myringitis Medical Condition
The occurrence of serious bullous myringitis complications remains rare because doctors provide treatment during the early stages of the disease. The medical condition develops into three different outcomes when patients do not receive treatment or they experience severe symptoms. The first outcome results in:
- Temporary hearing reduction
- Spread of infection to the middle ear
- Eardrum damage in rare cases
The medical condition shows decreased risk when doctors provide immediate treatment.
When to Seek Medical Care
Ear pain that is sudden, severe, or worsening should always be checked. This is especially true when pain follows a cold or flu-like illness.
Early diagnosis of bullous myringitis leads to faster relief and prevents unnecessary suffering.
Final Thoughts
Bullous myringitis is an ear drum infection which causes pain and develops blisters on the ear drum. The symptoms create strong sensations, but with proper treatment the patient outcomes remain highly positive.
The recovery process from bullous myringitis requires correct identification of symptoms and initiation of suitable treatment and administration of antibiotics when necessary. Both children and adults respond well, and bullous myringitis treatment in adults is especially effective when started early.
Most people achieve complete recovery with normal hearing and comfort after receiving prompt medical treatment.
FAQs
What is the cause of bullous myringitis?
Bullous myringitis is usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection that inflames the eardrum and leads to painful fluid-filled blisters.
What is the first line of treatment for bullous myringitis?
The first line of treatment is strong pain relief along with medical evaluation, followed by antibiotics if a bacterial infection is suspected.
What is the difference between otitis media and bullous myringitis?
Otitis media mainly involves infection and fluid behind the eardrum, while bullous myringitis specifically causes blistering and inflammation directly on the eardrum surface.
What happens if bullous myringitis is left untreated?
If left untreated, it can lead to prolonged pain, temporary hearing loss, and possible spread of infection into the middle ear.
Contact us
We are here for all your hearing needs, from hearing tests to hearing aids. Fill out the form below, and we will give you a call soon.
Please enter a valid mobile number with 10 digits.
Recent Blogs
By Team Hearzap | Jan. 28, 2026
By None | Jan. 27, 2026
By Team Hearzap | Jan. 23, 2026
By None | Jan. 22, 2026
By None | Jan. 20, 2026